Seamless
Connectivity
Features
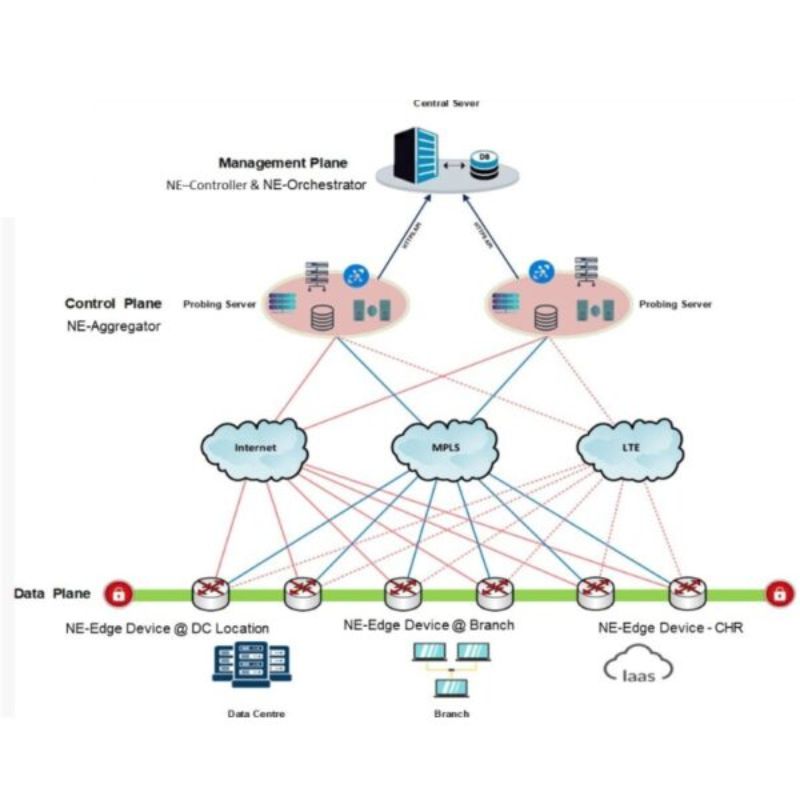
Controller & Orchestrator
- Serves as the first point of authentication
- Requires public IP address
- Zero Touch Provisioning
- Multi-Tenant Support
- Geo Mapping of Devices
- On-Cloud / In-Premise deployments
- Audit Logs
- Configuration Backup and Restore
- Central Configuration Management
- Edge Devices WebUI/CLI access
- Template Based Configuration
- RBAC
- NAC & WI-Fi Captive Portal
- Real-time monitoring & Reporting
- Notifications & Alerts
- SLA Reports
- Histograms

Aggregator
Aggregation: Combining multiple network connections or links (e.g., MPLS, broadband, cellular) to increase overall bandwidth and optimize network performance.
Traffic Optimization: Prioritizing and routing traffic based on application type, quality of service (QoS) requirements, and network policies.
Load Balancing: Distributing network traffic across available links to ensure efficient utilization and prevent congestion.
Failover and Redundancy: Providing failover capabilities to ensure continuous network connectivity even if one or more links experience disruptions.
Security: Implementing security features to protect against threats and ensuring data privacy.
Centralized Management: Offering centralized configuration and monitoring capabilities to streamline network administration.

Case Study
DVPL’s SDWAN NE-WAN
(Leading Co-Op Bank in India – 200 Locations)
Summary
Customer was looking for centralized visibility, control & security over
its network along with redundancy/fallback in last mile connectivity with
SLA monitoring
Challenges
Inconsistent connectivity
No redundancy in WAN Network
No uptime SLA/reports
No traffic prioritization
No centralized visibility/control over the entire network.
No alert mechanism during incidents
No redundancy in WAN Network
No uptime SLA/reports
No traffic prioritization
No centralized visibility/control over the entire network.
No alert mechanism during incidents
Solution
Multi fabric/media supportable CPE with B/w aggregation/auto failover to
avoid any
downtime
SLA Reports
QoS & Application/Traffic visibility
Encrypted VPN for end to end communication
Centralized visibility/control over the entire network
SLA Reports
QoS & Application/Traffic visibility
Encrypted VPN for end to end communication
Centralized visibility/control over the entire network

